fill_blind_pores¶
Remove any isolated void space (not connected to the boundary) from the image which is often needed such as for network extraction or direct numerical simulations
import numpy as np
import porespy as ps
import scipy.ndimage as spim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ps.visualization.set_mpl_style()
[19:10:28] ERROR PARDISO solver not installed, run `pip install pypardiso`. Otherwise, _workspace.py:56 simulations will be slow. Apple M chips not supported.
import inspect
print(inspect.signature(ps.filters.fill_blind_pores))
(im, conn: int = None, surface: bool = False)
im¶
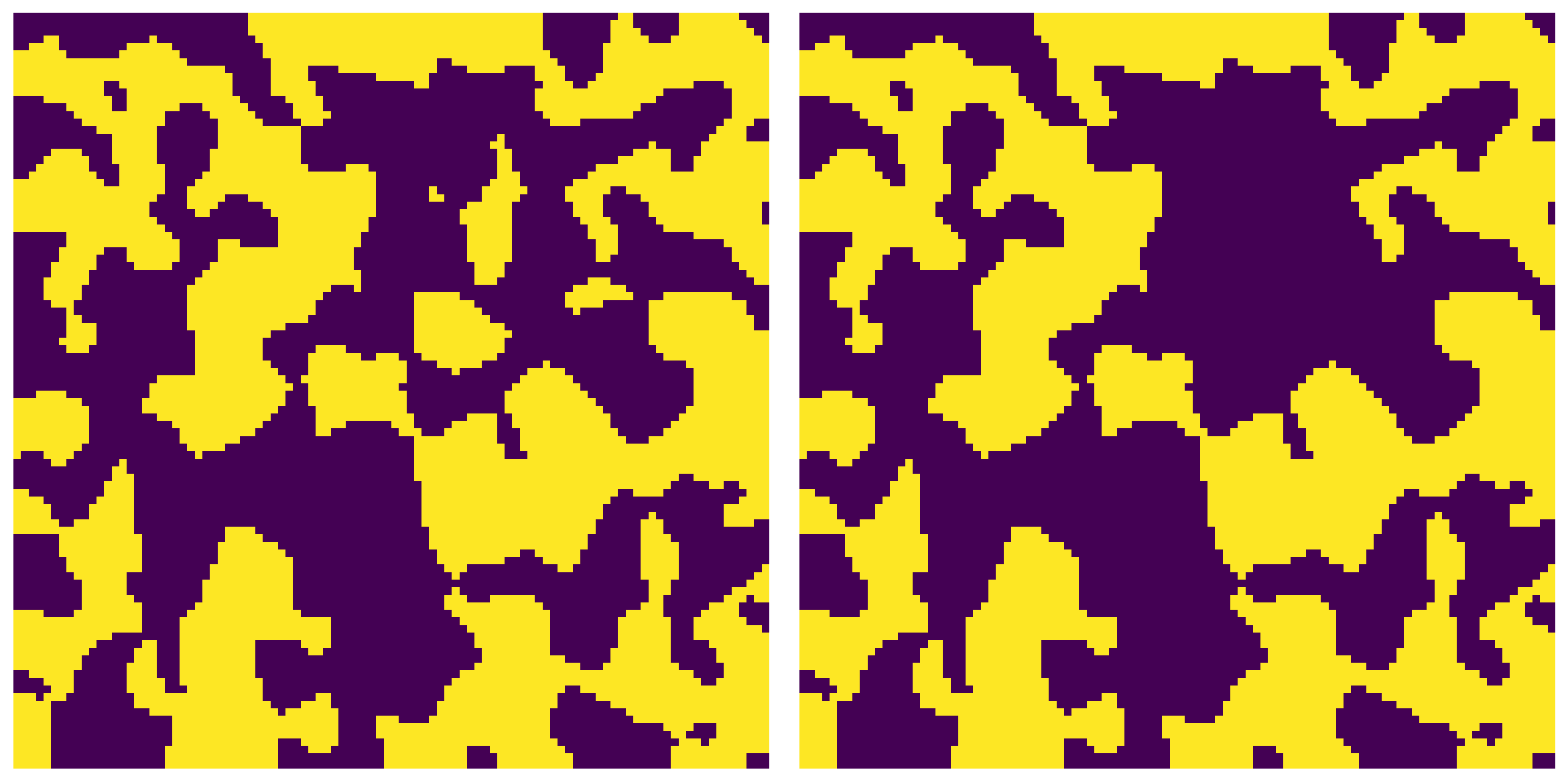
The void phase is indicated by True values. Blind pores are considered as any cluster of void voxels not connected to the boundary of the image.
np.random.seed(2)
im = ps.generators.blobs([100, 100], porosity=0.5)
im1 = ps.filters.fill_blind_pores(im)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[12, 6])
ax[0].imshow(im, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[1].imshow(im1, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
ax[1].axis(False);
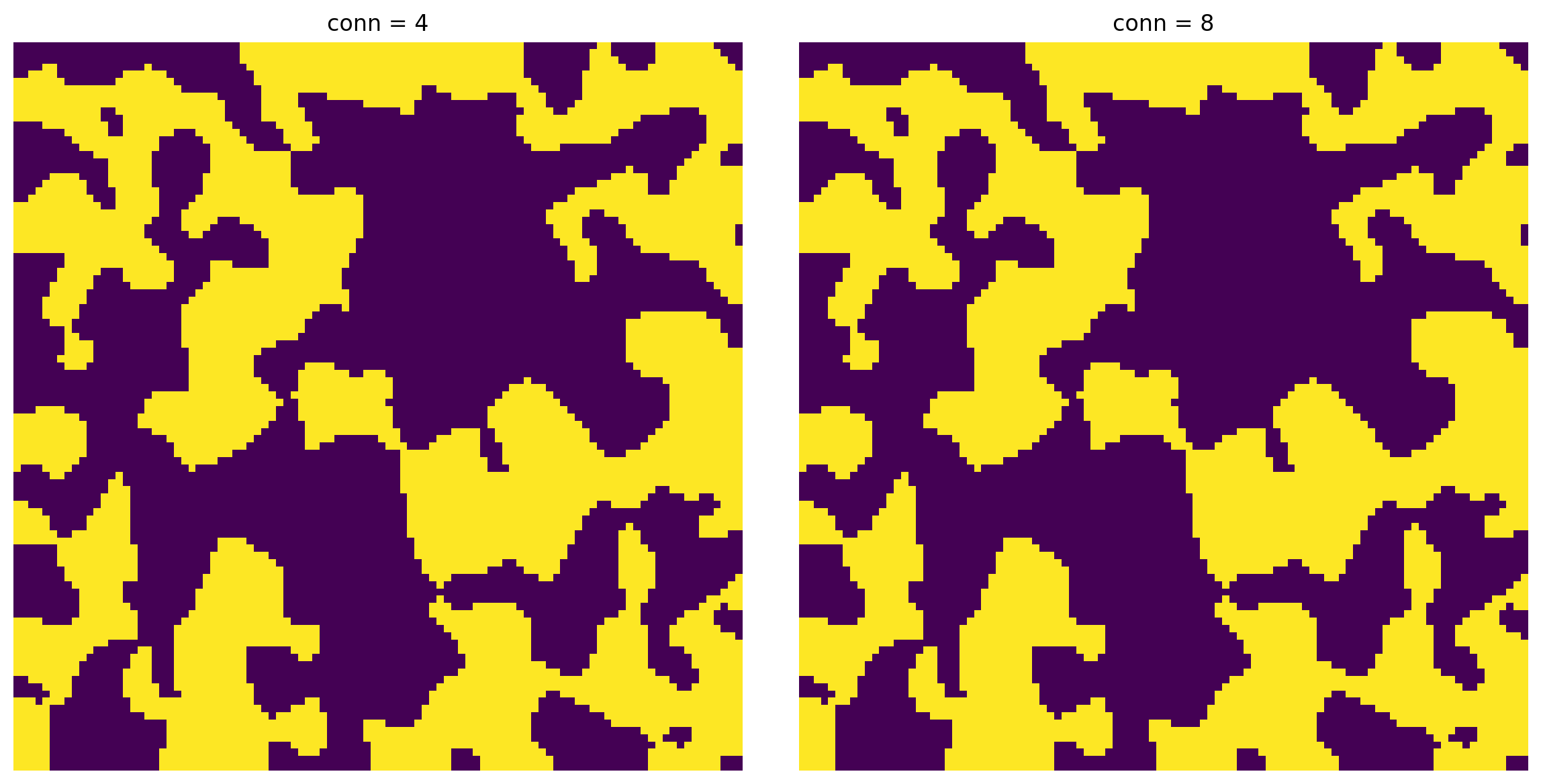
conn¶
Controls how ‘connected’ a group of voxels must be. In 2D the options are 4 and 8, while in 3D they are 6 and 26.
im1 = ps.filters.fill_blind_pores(im=im, conn=4)
im2 = ps.filters.fill_blind_pores(im=im, conn=8)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[12, 6]);
ax[0].imshow(im1, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title('conn = 4')
ax[1].imshow(im2, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title('conn = 8');
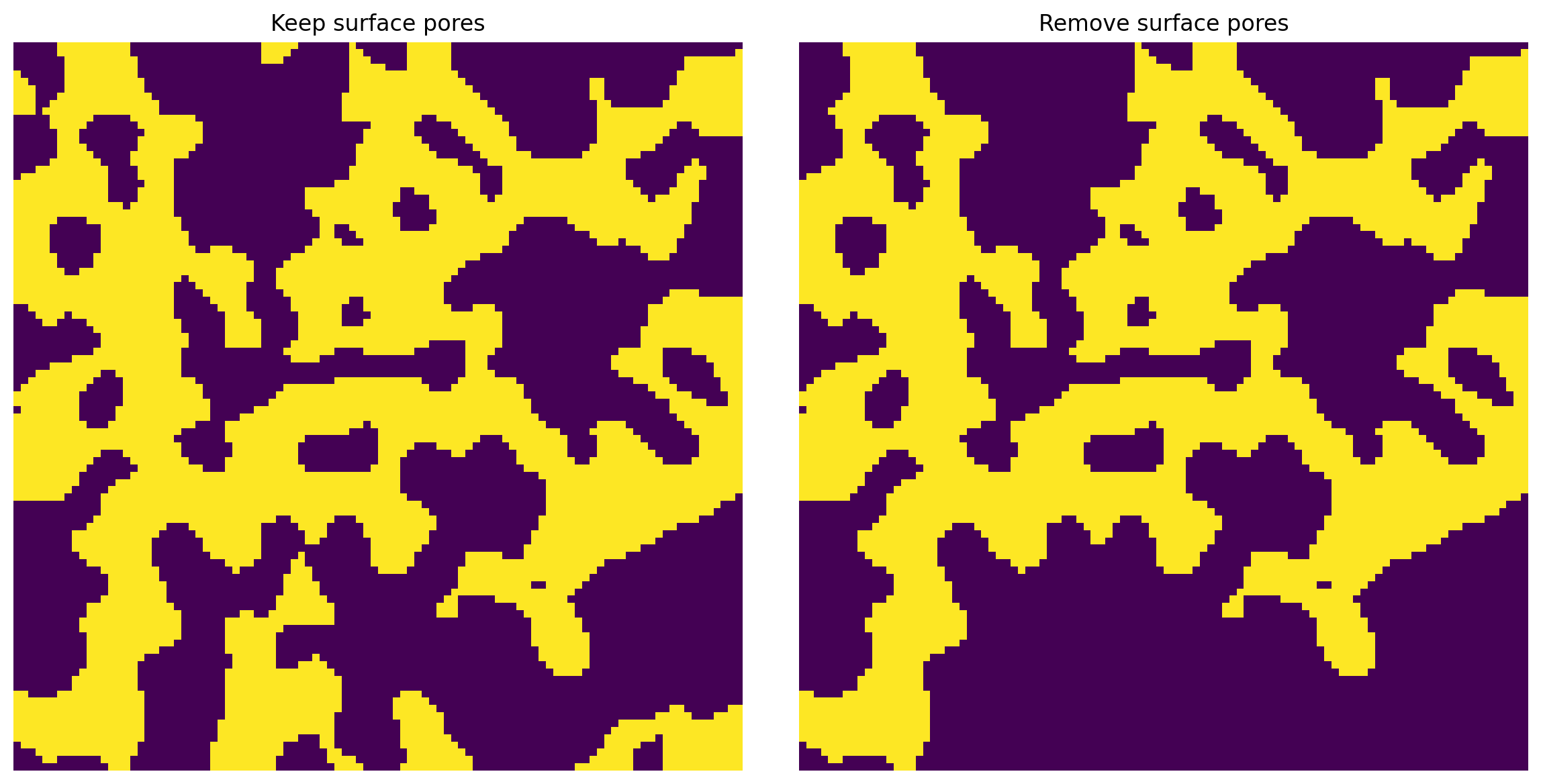
surface¶
This flag, then True also removes any void voxels that are on the surface but not connected to the main body of the void space. This option can produce mis-leading results since it basically just keeps the largest cluster. For better control it is recommended to use the trim_nonpercolation_paths function.
np.random.seed(0)
im = ps.generators.blobs([100, 100], porosity=0.5)
im1 = ps.filters.fill_blind_pores(im=im, surface=False)
im2 = ps.filters.fill_blind_pores(im=im, surface=True)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[12, 6]);
ax[0].imshow(im1, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title('Keep surface pores')
ax[1].imshow(im2, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title('Remove surface pores');