distance_transform_lin#
A variant of the standard distance transform where the distances are computed along a give axis rather than radially.
import numpy as np
import porespy as ps
import scipy.ndimage as spim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ps.visualization.set_mpl_style()
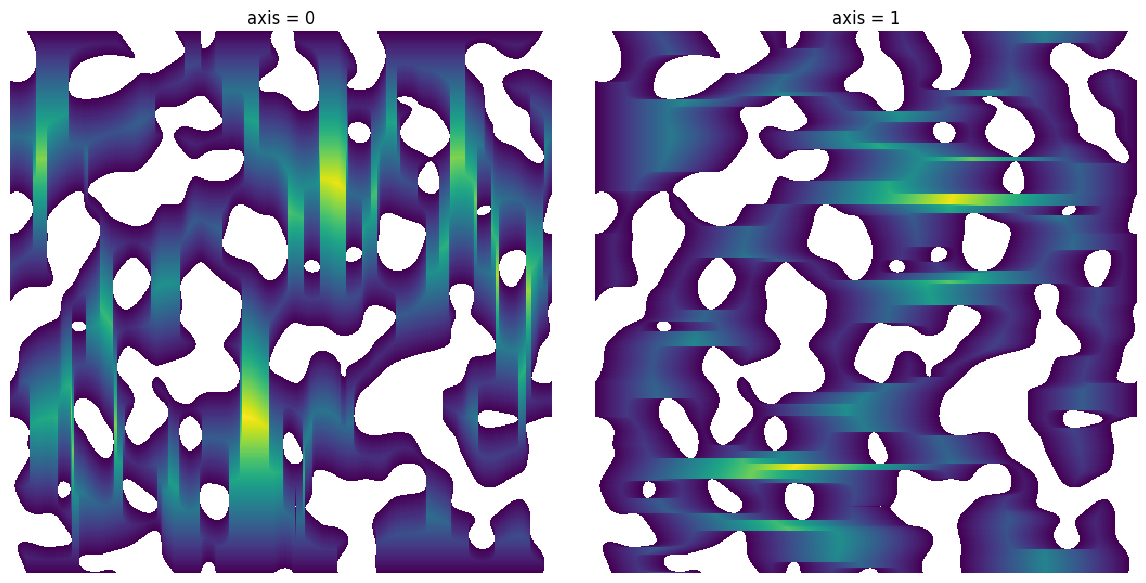
axis#
The axis along which the distances should be computed
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[12, 6])
im = ps.generators.blobs(shape=[500, 500], porosity=0.7)
axis = 0
dt = ps.filters.distance_transform_lin(im, axis=axis)
ax[0].imshow(dt / im)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"axis = {axis}")
axis = 1
dt = ps.filters.distance_transform_lin(im, axis=axis)
ax[1].imshow(dt / im)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"axis = {axis}");
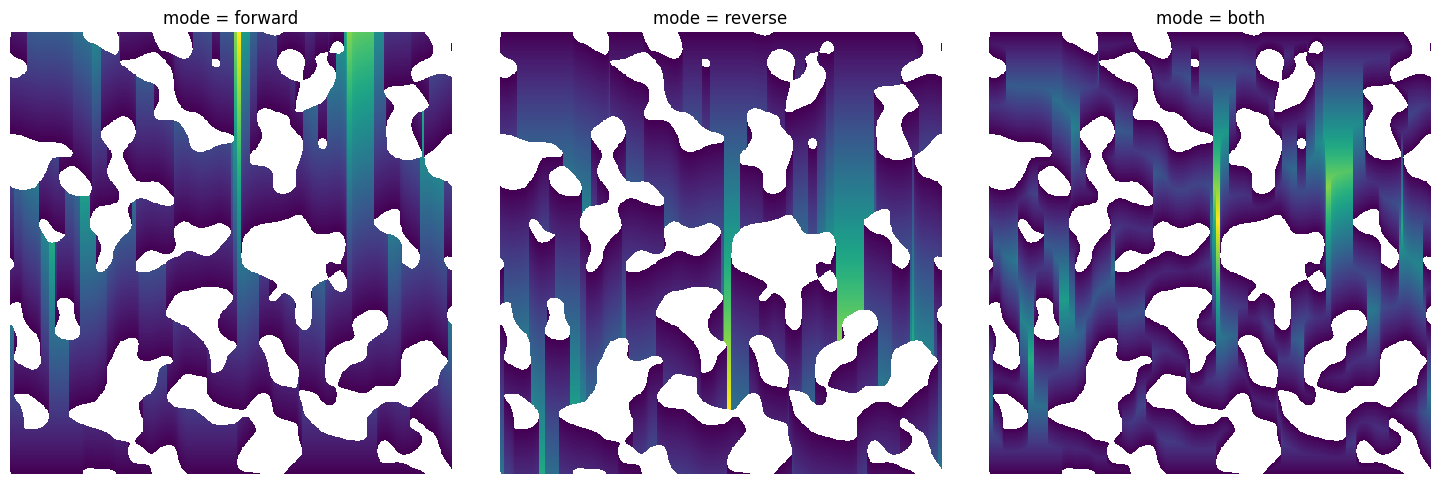
mode#
Whether the distances are comptuted from the start to end, end to start, or both.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=[15, 5])
im = ps.generators.blobs(shape=[500, 500], porosity=0.7)
mode = "forward"
dt = ps.filters.distance_transform_lin(im, mode=mode)
ax[0].imshow(dt / im)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"mode = {mode}")
mode = "reverse"
dt = ps.filters.distance_transform_lin(im, mode=mode)
ax[1].imshow(dt / im)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"mode = {mode}")
mode = "both"
dt = ps.filters.distance_transform_lin(im, mode=mode)
ax[2].imshow(dt / im)
ax[2].axis(False)
ax[2].set_title(f"mode = {mode}");

