hold_peaks#
Replaces each voxel with the last peak seen along the given axis
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from edt import edt
import porespy as ps
ps.visualization.set_mpl_style()
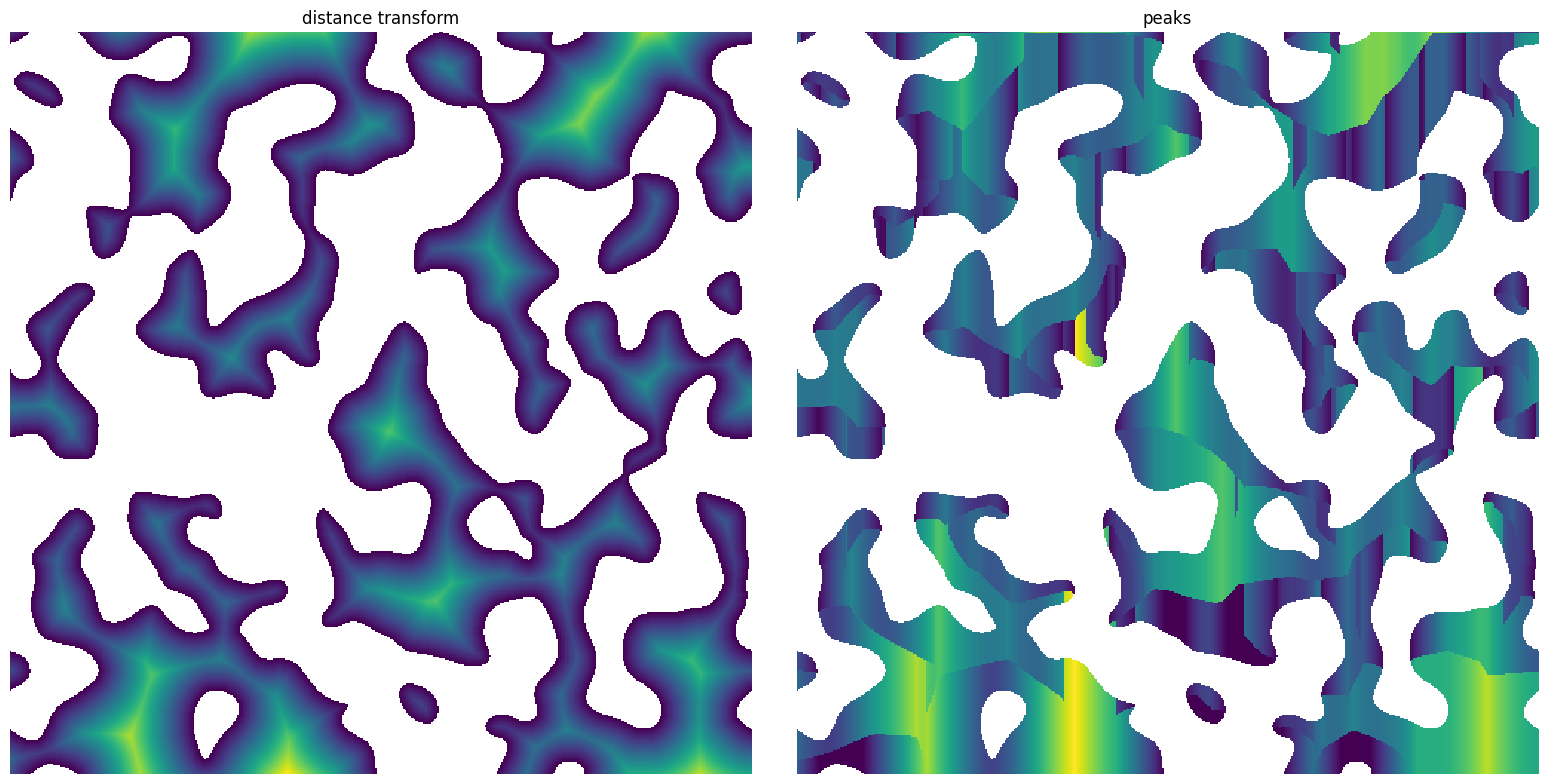
im#
The input image will most likely be the distant transform
np.random.seed(0)
im = ps.generators.blobs(shape=[500, 500])
dt = edt(im)
pk = ps.filters.hold_peaks(im=dt, axis=0)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[16, 8])
ax[0].imshow(dt / im)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title("distance transform")
ax[1].imshow(pk / im)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title("peaks");
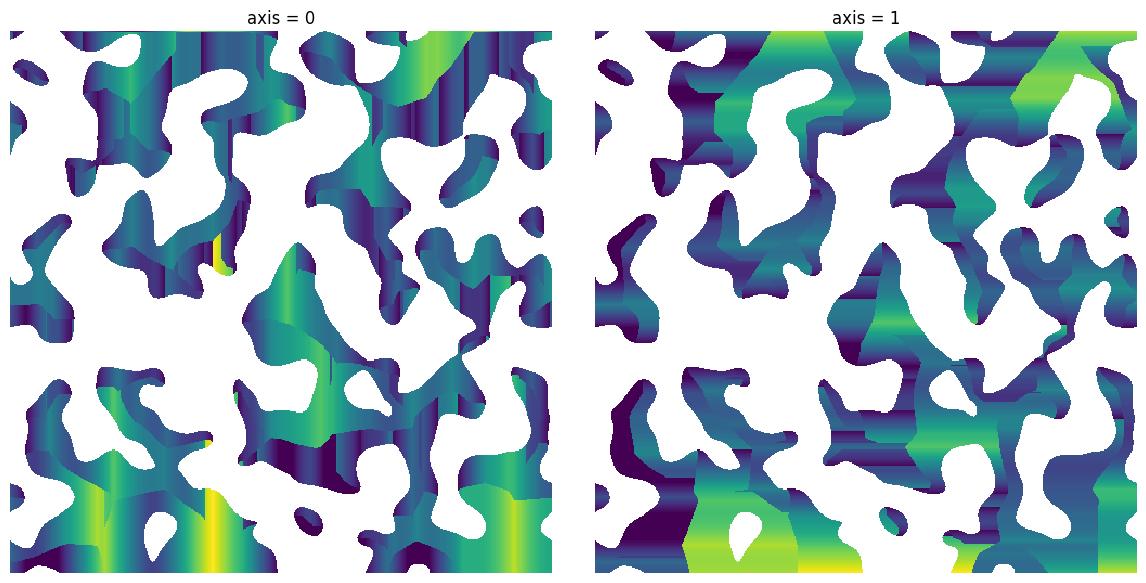
axis#
Controls the axis of the search:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[12, 6])
axis = 0
pk1 = ps.filters.hold_peaks(im=dt, axis=axis)
ax[0].imshow(pk1 / im)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"axis = {axis}")
axis = 1
pk2 = ps.filters.hold_peaks(im=dt, axis=axis)
ax[1].imshow(pk2 / im)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"axis = {axis}");
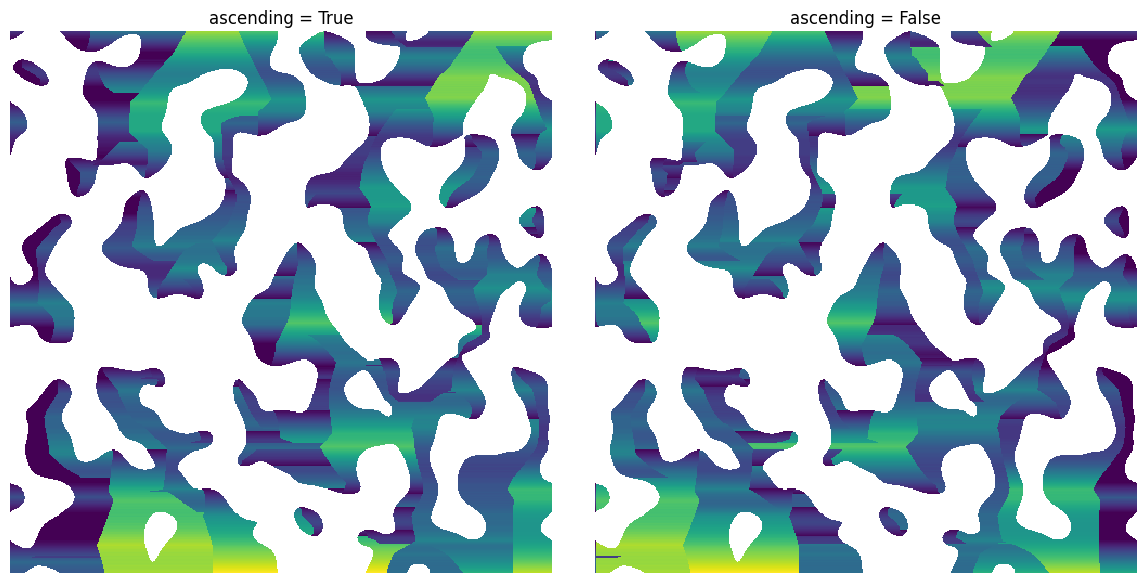
ascending#
A boolean that controls the direction of the scanning:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[12, 6])
ascending = True
pk1 = ps.filters.hold_peaks(im=dt, ascending=ascending)
ax[0].imshow(pk1 / im)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"ascending = {ascending}")
ascending = False
pk2 = ps.filters.hold_peaks(im=dt, ascending=ascending)
ax[1].imshow(pk2 / im)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"ascending = {ascending}");