rev_porosity#
Calculates the porosity of an image as a function subdomain size. This method works with extracting a specified number of subdomains of random size, then finding the porosity of those subdomains.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import porespy as ps
ps.visualization.set_mpl_style()
im#
The input binary image of the porous material with void space voxels labeled with 1(True) and solid phase labeled with 0(False).
np.random.seed(10)
im = ps.generators.blobs(shape=[100, 100, 100])
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=[4, 4])
ax.imshow(im[:, :, 6], origin="lower", interpolation="none")
ax.axis(False);

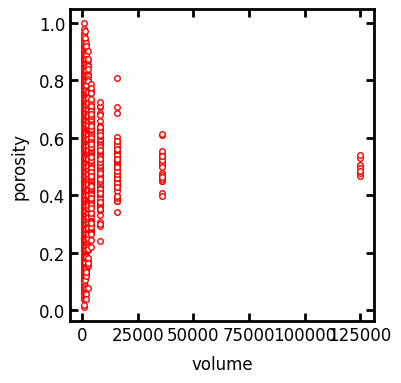
The rev_porosity returns a custom object containing the volume and porosity data. We can then plot the data to find the representative elementary volume (REV) of the porous material. REV can be found as the volume of a subdomain where any larger subdomain will have almost similar porosity values. In other words, in the following plot the point where the variation of porosity vs volume becomes a plateau.
rev = ps.metrics.rev_porosity(im=im)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=[4, 4])
ax.plot(rev.volume, rev.porosity, "r.")
ax.set_xlabel("volume")
ax.set_ylabel("porosity");
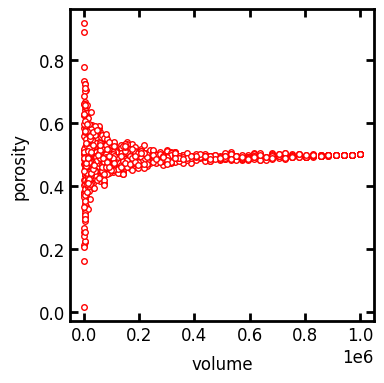
n#
By default the method uses 1000 randomly located and sized boxes to sample as subdomains. Let’s try a higher number to increase the number of samples:
rev = ps.metrics.rev_porosity(im=im, n=2000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=[4, 4])
ax.plot(rev.volume, rev.porosity, "r.")
ax.set_xlabel("volume")
ax.set_ylabel("porosity");
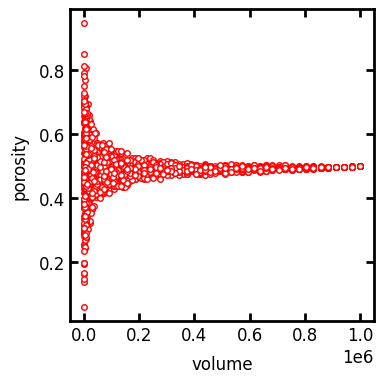
slices#
Instead of specifying n randomly located and sized boxes, you can also provided a list containing slice objects that define custom boxes. There are some functions in porespy.tools for creating such lists, such as get_slices_mulitgrid:
slices = ps.tools.get_slices_multigrid(
im=im,
block_size_range=[10, 50],
)
rev = ps.metrics.rev_porosity(im, slices=slices)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=[4, 4])
ax.plot(rev.volume, rev.porosity, "r.")
ax.set_xlabel("volume")
ax.set_ylabel("porosity");