overlapping_spheres#
Generates overlapping spheres by inserting random points then dilating them to the specified radius.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import porespy as ps
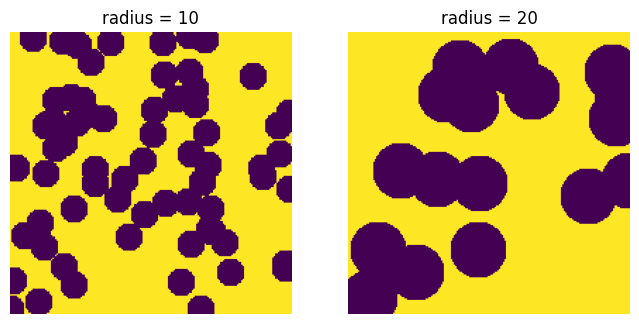
radius#
Controls the size of the spheres:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[8, 4])
shape = [200, 200]
e = 0.6
r = 10
im1 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e)
ax[0].imshow(im1)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"radius = {r}")
r = 20
im2 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e)
ax[1].imshow(im2)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"radius = {r}");
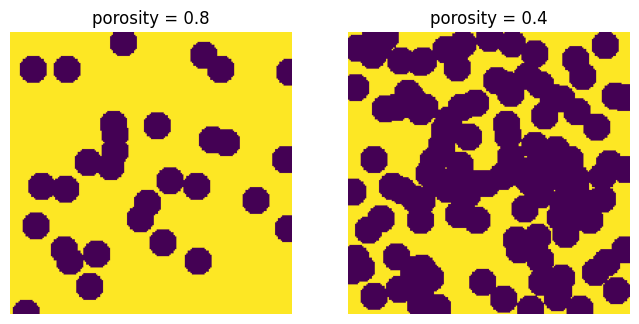
porosity#
The number of spheres added is adjusted by meet the requested porosity:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[8, 4])
r = 10
e = 0.8
im1 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e)
ax[0].imshow(im1)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"porosity = {e}")
e = 0.4
im2 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e)
ax[1].imshow(im2)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"porosity = {e}");
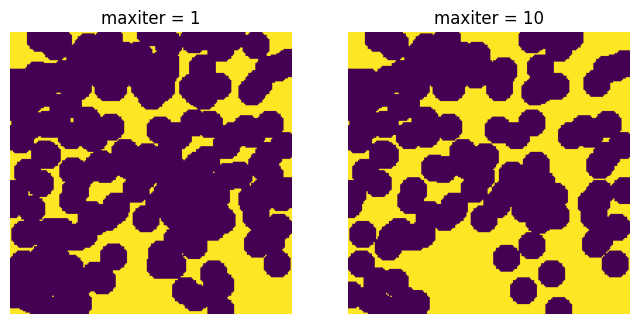
max_iter#
Because the spheres overlap randomly, it’s not possible to match the desired porosity perfect so a trial and error approach is used. This parameters control the maximum number of iterations used to match the desired porosity within the specified tolerance.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[8, 4])
print("target porosity =", e)
np.random.seed(0)
mi = 1
im1 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e, maxiter=mi)
ax[0].imshow(im1)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"maxiter = {mi}")
print("porosity = ", ps.metrics.porosity(im1))
np.random.seed(0)
mi = 10
im2 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e, maxiter=mi)
ax[1].imshow(im2)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"maxiter = {mi}")
print("porosity = ", ps.metrics.porosity(im2))
target porosity = 0.4
porosity = 0.26175
porosity = 0.406125
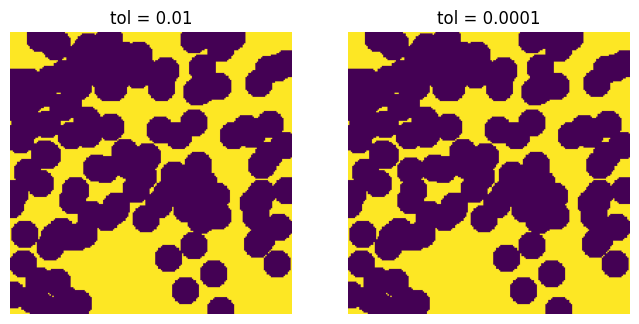
tol#
Tolerance for porosity relative to input value. If requesting a porosity of 0.5, then tol=0.1 will halt the iteration once the porosity is within 10% of the desired value, so between 0.45 and 0.55. Note that the procedure may also stop early if maxiter is reached first.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[8, 4])
print("target porosity =", e)
np.random.seed(0)
t = 1e-2
mi = 100
im1 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e, maxiter=mi, tol=t)
ax[0].imshow(im1)
ax[0].axis(False)
ax[0].set_title(f"tol = {t}")
print("porosity = ", ps.metrics.porosity(im1))
np.random.seed(0)
t = 1e-4
im2 = ps.generators.overlapping_spheres(shape=shape, r=r, porosity=e, maxiter=mi, tol=t)
ax[1].imshow(im2)
ax[1].axis(False)
ax[1].set_title(f"tol = {t}")
print("porosity = ", ps.metrics.porosity(im2))
target porosity =
0.4
porosity = 0.406125
porosity = 0.400225